How We Make Policy
The Policy-Making Process
In making Irish regulatory policy, we follow principles of good regulation. The process is a continuous one and typically follows this life cycle:
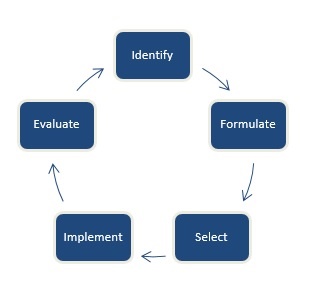
When we identify a policy issue through analysis and risk assessment, we work to understand its underlying causes and determine whether intervention by the Central Bank is needed.
We then formulate a set of options that could address the issue in an effective, and proportionate way. We assess the risks and benefits and compile a set of policy options to respond. Where appropriate, the Central Bank consults with interested parties during policy development in order to seek, receive, analyse and respond to feedback from all interested and affected parties on what policy response or codes, standards, regulations or guidelines would be most effective and proportionate. These consultations inform the decision-making process.
After consideration of the options, and informed by evidence obtained, we select the preferred policy option.
The policy is made public and implemented. It is subject to supervision and enforcement as appropriate. We continually evaluate whether existing regulatory policy is effectively meeting our Mission Statement. We serve the public interest by maintaining monetary and financial stability while ensuring that the financial system operates in the best interests of consumers and the wider economy.
Governance
When developing policy, the Central Bank engages with a range of national stakeholders, notably the Department of Finance, and consumer and industry representative organisations.
Public consultations are also held on significant policy initiatives. Our procedures in relation to consultation policy are set out in the Central Bank of Ireland Policy on Consultations.
Within the Central Bank, the Policy Committee advises the Deputy Governor (Financial Regulation) on supervisory and regulatory policy. Chaired by the Deputy Governor (Financial Regulation), the Policy Committee comprises of the Regulatory Directors, the Chief Economist and relevant Heads of Division from across the Central Bank. Policy initiatives are formally adopted by the Central Bank Commission, the Deputy Governor (Financial Regulation), or responsible directors with delegation.
Influencing EU and global policy-making
The Central Bank actively engages in the development of relevant laws, regulations and technical standards in Europe via working groups in the Council of the European Union, the European Commission, the European Supervisory Authorities, and the European Systemic Risk Board. It influences the development of international principles for regulation by its participation in international bodies including the International Organisation for Securities Commissions, Financial Action Taskforce and FinCoNet. More detail on the Central Bank’s participation in these organisations is provided on the EU and International Policy page.
Reporting and accountability
Each year, in addition to its Annual Report, the Central Bank must prepare an Annual Performance Statement on its financial regulatory activities and its plans for the year ahead.
The Central Bank is required to have an international peer review of its regulatory performance carried out at least every four years.